AGROVOLTAICS REALISATIONS
Basic installation
Agrovoltaics: a Solar Innovation
1) Solar Panels on Agricultural Land
When Solar Panels are installed for a long duration on Agricultural land , the agricultural organizations are frustrated because they think about losses of land, and of food production for people or animals.
They fear the agricultural structure will disintegrate and that the land is no more available for sustainable development of farms
Today there is an energy transition from fossil and nuclear energy towards renewable energy . Agriculture and horticulture will play an important role in it.
The agricultural sector furthermore has to lower the emission of greenhouse gases.
Solar panels installed on agricultural land are the answer to these questions.
Today there exist innovative technologies to combine solar energy with agricultural land.
2) Solar panels on agricultural land: double yield
On a piece of agricultural land 2 complementary products can be produced:
- Photovoltaic energy
- Agricultural products
The photovoltaic energy serves for the production of electricity.
Agricultural products are food for human and animals.
It is essential that crops are selected who have a higher photosynthetic yield than grasses and have a maximum dissolution of CO2 and a production of Carbon.
Plants which are selected today are: potatoes, sugar beets, soy, winter wheat, rape seed asparagus, pears, salsifies, fruit in general … depending on the reduced solar irradiation and the water balance.
Since photosynthesis takes place in the leaves of plants, many crops have a better global photosynthesis result than grasses.
Agrovoltaics is in a partnership with the Catholic University of Leuven (KUL) in the research to determine the best crops for each specific agricultural environment and climate.
The project is called Tetra Agrivoltaics
2.1 Configuration of solar panels
Many set-ups of photovoltaic panels have been designed.
They are installed on piles with a free height of 2.5 meter and supporting 3x4 panels on 2 driven piles with a distance of about 6 meter between the rows.
Between and under the panels crops can be seeded, grown and harvested with adapted agricultural machines. In this way Agrovoltaics realizes an upgrade of the meadows and the land all over the globe.
Some pictures of the Agrovoltaics prototype models hereunder demonstrate this:

Pear cultivation with semi-transparent panels in Europe

Beet cultivation in Western Europe with bifacial solar panels
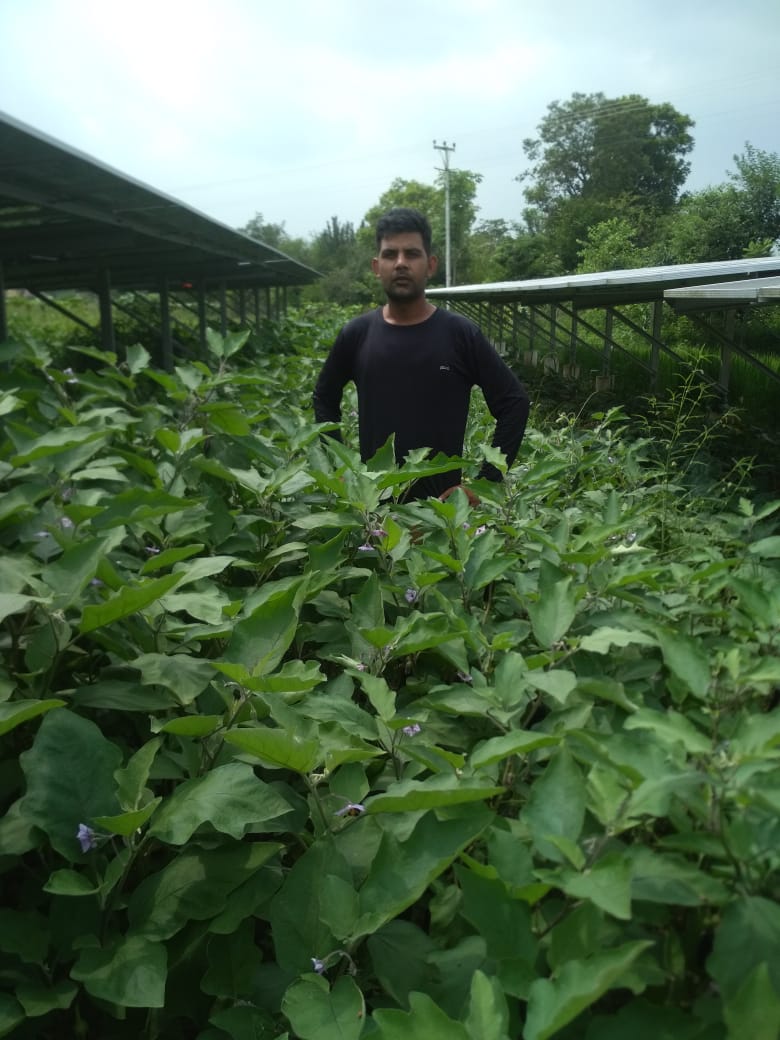

Brinjal (eggplant) crop with standard panels India
2.2 Business case: Agrovoltaic field of 10 hectare, 100.000 sqm
The panels are mounted on piles with a length of about 4.5 meter, about 2 m in the ground and 2.5 m free height. The panels are installed with an inclination of 10 to 30 degrees and a distance between the rows of 6 m. In this way 10 MW can be installed.
Four panels of 200x100 are installed above each other in a landscape position and 3 next to each other , so there are 12 panels for each basic structure which is supported by 2 piles.
This position is defined to seed and harvest crops over the complete surface of the agricultural land.
By this positioning 25.000 panels of 400 Watt peak of 2 meters can be installed with a total output of 10 Megawatt.
Costs and revenue of such an installation are the following:
- The expected energy production is 10 million KWh..
- The investment cost price is around 6 million euro all in.
- The price of the photovoltaic current to the end consumer is 3.9 Eurocent per KWH.
- The financial yield of the crop is around 2000 euro per hectare year.
This is acceptable for injection in the grid.
The value of the electricity for a direct supply to the customer is 6 ct per Kwh which increases the final results.
Download Triple Solar - Business ModelAgrovoltaics has presently several Megawatt Projects under development.
3. Electricity, food and drinkable water: 3 functional solar system
Lay out of a triple usage Photovoltaic plant 100 Megawatt.